Properties of sound.
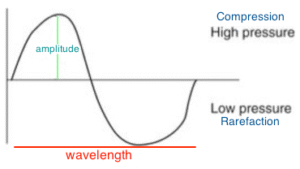
Sound is a mechanical, longitudinal wave. Longitudinal means parallel from sound source. Mechanically moves through medium by vibration of molecules or physically changing pressure, compressions (high pressure) and rarefactions (low pressure) One complete cycle = 1 compression and 1 rarefaction
Frequency = # cycles per second Hz.
Wavelength = length of one cycle mm
Period = time of one cycle µs
ƛ = wavelength
ƛ = c/f
c = prop speed | f = frequency
Relationships
Direct: If one increases, the other increases and vice versa (go together)
Inverse: If one increases, the other decreases (opposites)
Wavelength depends on 2 things – frequency (determined sound source) and propagation speed (determined by medium)
Wavelength and frequency are inversely related
Wavelength directly related to propagation speed
Mediums with fast prop speed = longer wavelength
Mediums with slower prop speed = shorter wavelength
Propagation speed is NOT affected by either freq or wavelength